(en español aquí)
We have just published a new paper in the journal Revista de Climatología (ISSN 1578-8768) . This paper presents a new time series of September Arctic sea ice extent from 1935 to 2014:
– Download full text (pdf, in spanish)
– Download extent data values (CSV)
– Download gridded data (NetCDF)
Abstract
Since 1979 satellite-borne passive microwave sensors have provided a continuous and consistent record of Arctic sea ice extent. This record shows a significant downward trend, particularly at September, when Arctic sea ice reaches its annual minimum. Records before 1979 exist, but are not consistent with the satellite record and have limited reliability, specially before 1953. We present a new time series of September Arctic sea ice extent from 1935 to 2014 that includes data for the Siberian sector (AARI operational charts) not used previously in the Arctic wide existing time series (Walsh, HadISST). The new record has been adjusted to be consistent with satellite data. The trend for 1935-2014 is -3.5% decade, while the trend for the satellite era is -13.3% decade. However, the trends since 1935 until early 1980s are positive and statistically significant. The trends turn negative in the 1990s, reaching statistical significance from 2006 onwards. The lowest annual minimum in the pre-satellite era is higher than any annual minimum after 2001.
Methodology
STEP 1: We adjusted HadISST (1953-1978) to match the satellite data, using the same method employed by Meier et al. 2012 . However, we adjusted the gridded data as well, instead of adjusting only the extent values as Meier et al. did:

Arctic sea ice concentration for September 1960. Left: original HadISST. Right: HadISST after the adjustment to match the satellite data.
—————————————————————————————————-
STEP 2: We incorporated AARI data into previously adjusted HadISST (1953-1978):
———————————————————————————————————
STEP 3: We extend back the time series to 1935, combining AARI data with a climatology (calculated on the basis of the correlation between sea ice extent and surface air temperature):

Left: September climatology for the 1935-1952 period . Right: Arctic sea ice extent for September 1952, after the incorporation of AARI data into the climatology.
Results
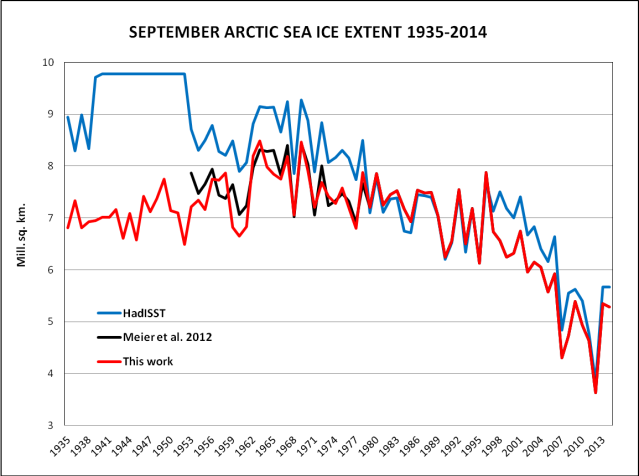
September Arctic sea ice extent from 1935 to 2014:
—————————————————————————————————–
September Arctic sea ice extent since 1935 to 2014. Red: this work. Black: Meier et al. Blue: HadISST:
—————————————————————————————————–
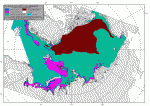
Median September Arctic sea ice extent for the lowest decade of the pre-satellite era (1935-1944, left) and for the lowest decade of the satellite era (2005-2014, right):
 ————————————————————————————————
————————————————————————————————
September Arctic sea ice extent since 1935 to 2014. Black line: this work. Blue line: HadISST. Grey band: estimated sea ice extent using a regression of September SIE on Arctic surface air temperature data (Apr-Sept., 70-90N, CRUTEM4) based on the correlation between sea ice extent and air temperature during the satellite era:
 ——————————————————————————————————
——————————————————————————————————
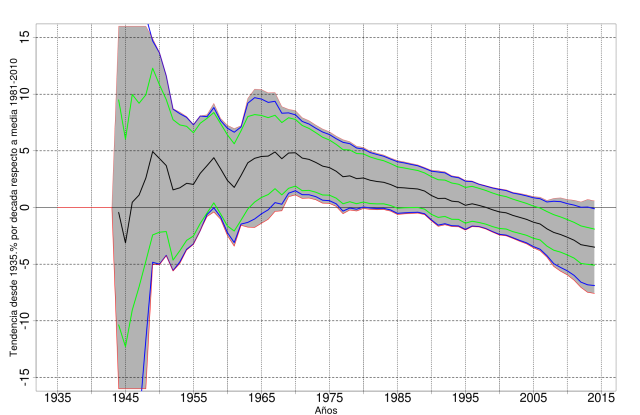
The graph below shows the evolution of the trend as years are added to the end of a time series starting in 1935. The first point of the black line shows the trend of a 10-yr time series (1935–1944), and subsequent points extend the time series by one year each up to a trend over the full 80-yr 1935–2014 time series. The green, blue and red lines represent the 99% confidence level according to three different methods (according to the first method, an upward trend is significant when both green lines are above zero, and a downward trend is significant when both green lines are below 0; the same applies to blue and red lines with the other two methods):
Cea-Pirón, MA and Cano-Pasalodos, JA (2016): Nueva serie de extensión del hielo marino ártico en septiembre entre 1935 y 2014. Rev. Climatol., 16: 1-19 .














































http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.44756
http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.44757
http://dx.doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.44758
http://neven1.typepad.com/blog/2016/01/september-arctic-sea-ice-extent-1935-2014.html
New Walsh dataset:
– Paper: http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1931-0846.2016.12195.x/abstract
– Data: https://nsidc.org/data/g10010
Pingback: The new Walsh dataset: Arctic sea ice extent since 1850 | Banquisa en el Ártico: el blog del hielo marino
Updated until 2016:
Pingback: Nueva serie de extensión del hielo marino ártico en septiembre entre 1935 y 2014 | Banquisa en el Ártico: el blog del hielo marino
Cited by
Mueller, B. L. (2016). Attribution of Arctic sea ice decline from 1953 to 2012 to influences from natural, greenhouse-gas and anthropogenic aerosol forcing (Doctoral dissertation).
https://dspace.library.uvic.ca:8443/handle/1828/7669
Cited by
Connolly, R., Connolly, M., & Soon, W. (2017). Re-calibration of Arctic sea ice extent datasets using Arctic surface air temperature records. Hydrological Sciences Journal.
http://www.tandfonline.com/doi/abs/10.1080/02626667.2017.1324974
Updated until 2017:
Cited by:
MUELLER, Bennit L., et al. Attribution of Arctic Sea Ice Decline from 1953 to 2012 to Influences from Natural, Greenhouse Gas, and Anthropogenic Aerosol Forcing. Journal of Climate, 2018, vol. 31, no 19, p. 7771-7787.
https://doi.org/10.1175/JCLI-D-17-0552.1
Updated to 2018:
Updated to 2019:
Updated to 2020:

Updated to 2021:
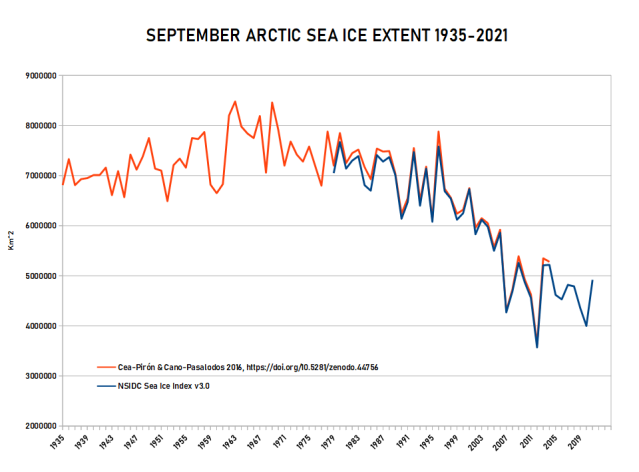
September Arctic sea ice extent, 1935 – 2021
Cited by:
Barry, R., & Gan, T. (2022). The Global Cryosphere: Past, Present, and Future (2nd ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. doi:10.1017/9781108767262
https://www.cambridge.org/core/books/the-global-cryosphere/A174F8EAA3AD240AD7B24D8F070B7280
https://books.google.es/books?id=IARsEAAAQBAJ&printsec=frontcover&hl=es#v=onepage&q&f=false
Updated to 2023.
September Arctic sea ice extent 1935 – 2023 :